Cosmetic moulding, especially in plastic injection moulding, requires high precision and aesthetic quality. Even minor surface defects can render a product unacceptable for consumer use. Below are some of the most common defects encountered in cosmetic moulding along with their likely causes:
1. Flow Lines
Description: Streaks or patterns (often wavy) that appear on the surface, usually around gates or thin sections.
Causes:
Low injection speed or pressure
Material temperature too low
Poor gate design or improper gate location
Mold temperature too low
2. Sink Marks
Description: Small depressions or dimples on thick sections of the moulded part.
Causes:
Insufficient cooling time
Inadequate packing pressure
Thick part geometry without sufficient ribbing
Mold temperature too high
3. Weld Lines (Knit Lines)
Description: Lines or seams where two flow fronts meet, often visible as a cosmetic imperfection.
Causes:
Low melt or mold temperature
Low injection speed
Poor venting
Design features that force multiple flow fronts to converge
4. Jetting
Description: Worm-like flow patterns on the part’s surface.
Causes:
High injection speed with low melt viscosity
Improper gate design (too small or in the wrong location)
Inadequate mold temperature
5. Blush Marks
Description: Whitish or dull area, usually near the gate.
Causes:
Excessive shear stress due to high injection speed
Improper gate size or design
Material degradation
6. Splay (Silver Streaks)
Description: Streaks or lines, typically silvery, that appear on the part’s surface.
Causes:
Moisture in the resin
Degraded material due to excessive heat
Air entrapment
Contaminated resin
7. Burn Marks
Description: Dark, often black or brown, discoloration caused by trapped gases.
Causes:
Inadequate venting
Excessive injection speed or pressure
Trapped air overheating due to compression
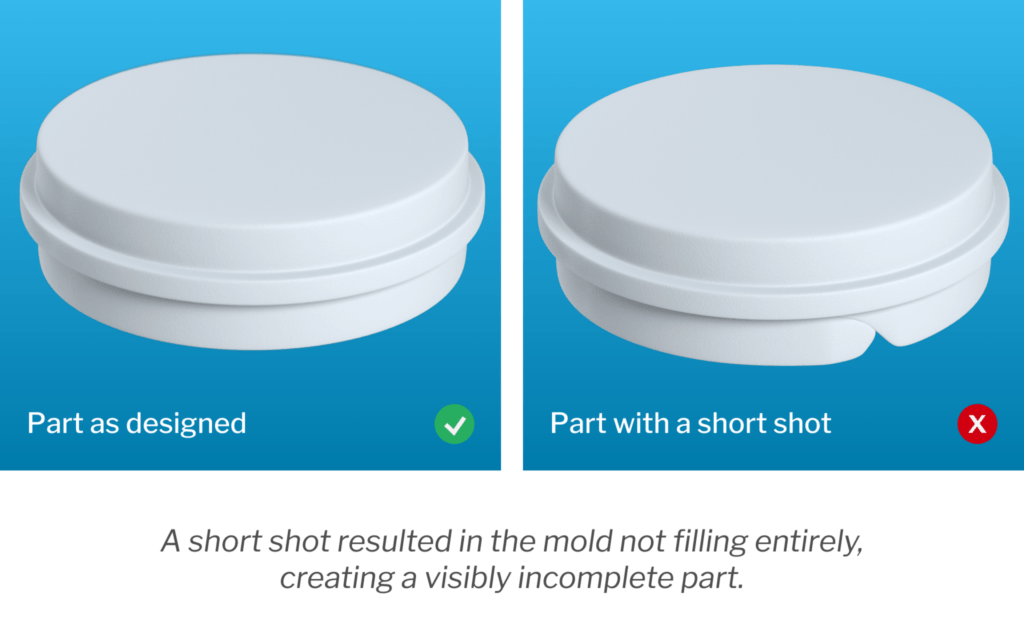
8. Short Shots
Description: Incomplete filling of the mold cavity, leading to missing sections.
Causes:
Low injection pressure or speed
Low melt or mold temperature
Flow restrictions due to poor part design
Inadequate venting
9. Flash
Description: Excess material that escapes from the mold cavity and solidifies on the parting line.
Causes:
Worn or damaged mold components
Excessive injection pressure
Improper clamping force
Mold not properly aligned
10. Warping
Description: Twisting or deformation of the part after cooling.
Causes:
Uneven cooling across the part
Incorrect mold temperature
Inconsistent wall thickness
High shrinkage materials
Preventive Measures
To minimize cosmetic defects:
Maintain optimal processing parameters (temperature, pressure, speed).
Ensure proper mold design and maintenance.
Use quality raw materials and dry them thoroughly.
Design parts with uniform wall thickness and proper flow paths.
Use simulation software to predict potential defects before manufacturing.