1. Introduction
In both die casting and moulding processes, the gating system plays a crucial role in controlling how molten metal or plastic enters the mould cavity. A well-designed gating system ensures efficient flow, minimizes defects, and improves the quality of the final casting.
2. What is a Gating System?
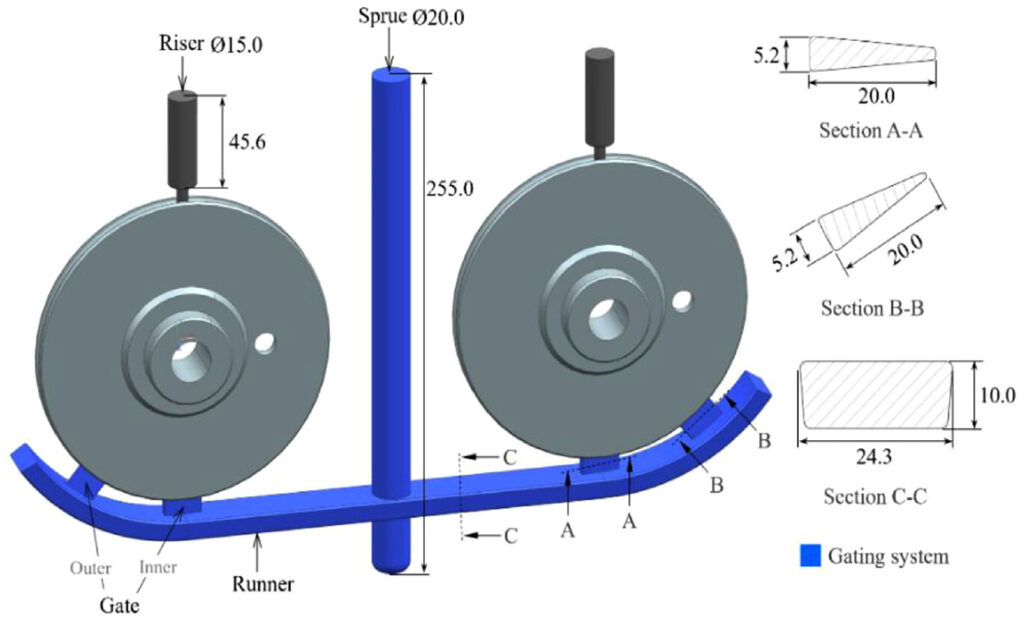
A gating system is a network of passages through which the molten material (metal or plastic) flows from the pouring basin or injection unit into the mould cavity.
It typically includes:
Pouring Basin / Shot Sleeve
Sprue
Runner
Gate
Overflow wells (mainly in die casting)
3. Functions of a Gating System
Directs flow of molten material into the mould.
Controls the rate of filling to avoid turbulence and air entrapment.
Filters impurities (with filters or traps).
Reduces shrinkage defects and cold shuts.
Helps in solidification control, reducing hot spots.
Allows venting of gases from the mould cavity.
4. Components of a Gating System
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Pouring Basin | Initial reservoir for molten metal; reduces splash. |
| Sprue | Vertical channel that directs flow downwards. |
| Runner | Horizontal channel that carries molten metal from sprue to gate(s). |
| Gate | Narrow opening that feeds molten material into the mould cavity. |
| Vent | Allows trapped air/gas to escape. |
| Overflow / Cavity Wells | Collect excess metal and reduce defects (mainly in die casting). |