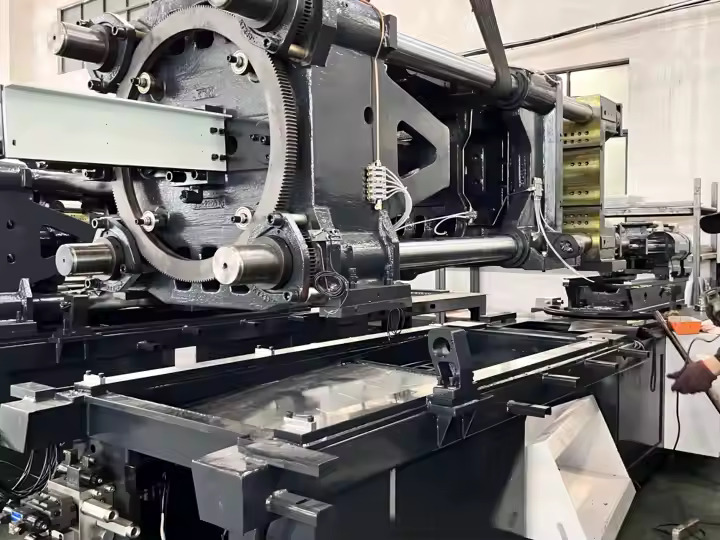
Low-Temperature PVC Molding Techniques
Low-temperature Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) molding is an efficient manufacturing process used to produce flexible, durable, and cost-effective components for various industries, including automotive, medical, construction, and consumer goods. By optimizing molding techniques at lower processing temperatures, manufacturers can reduce energy consumption, minimize thermal degradation, and enhance material properties.
Key Advantages of Low-Temperature PVC Molding
✅ Energy Efficiency – Lower processing temperatures reduce power consumption, cutting operational costs.
✅ Minimized Thermal Degradation – Prevents material breakdown, ensuring consistent quality and longevity.
✅ Improved Surface Finish – Reduces defects like burn marks, warping, or brittleness in molded parts.
✅ Extended Mold Life – Less heat stress on molds leads to longer tool lifespan and reduced maintenance.
Common Low-Temperature PVC Molding Techniques
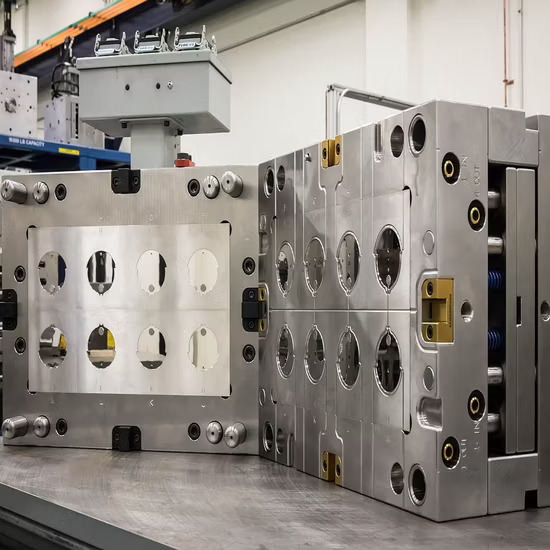
Injection Molding
- Uses precisely controlled heating and cooling to mold complex PVC components.
- Ideal for medical tubing, automotive trims, and electrical housings.
- Processing Temperature: 140–190°C (284–374°F) for standard flexible PVC.
Compression Molding
- Best suited for thicker, large-format PVC parts like gaskets and seals.
- Requires low pressure and moderate heat, reducing material stress.
- Processing Temperature: 120–160°C (248–320°F).
Extrusion Molding
- Used for PVC pipes, window profiles, and wire coatings.
- Continuous processing allows for uniform wall thickness and structural integrity.
- Processing Temperature: 130–170°C (266–338°F).
Rotational Molding
- Best for hollow PVC products like storage tanks and protective casings.
- Involves slow heating and rotation to distribute material evenly.
- Processing Temperature: 120–160°C (248–320°F).
Optimizing Low-Temperature PVC Molding
🔹 Use Plasticizers & Additives – Enhances flexibility, impact resistance, and flame retardancy.
🔹 Improve Cooling Systems – Faster cooling helps maintain precision and reduce cycle times.
🔹 Maintain Mold Surface Temperature – Proper mold heating prevents flow defects and weak spots.
🔹 Adjust Screw & Barrel Design – Ensures smooth material flow and homogeneity.