Parison Formation refers to the process of creating a hollow tube of molten plastic, called a parison, which is a precursor in blow molding operations. This parison is later inflated inside a mold cavity to form hollow plastic products such as bottles, containers, and tanks.
Types of Parison Formation Methods
Extrusion Blow Molding (EBM)
A continuous or intermittent parison is extruded through a die.
Common for producing bottles, drums, and fuel tanks.
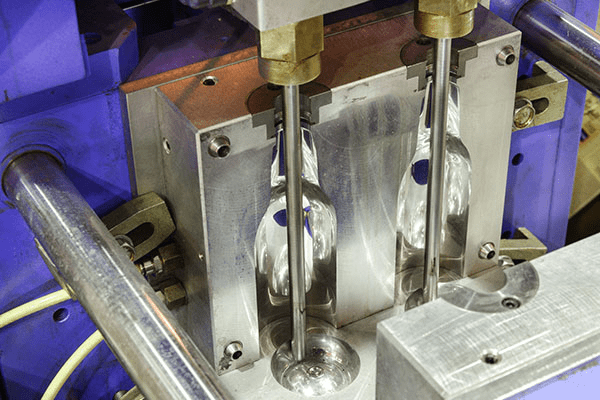
Injection Blow Molding (IBM)
A parison (also called a preform) is injection-molded and then transferred to a blow mold.
Used for precise, small containers like pharmaceutical bottles.
Stretch Blow Molding (SBM)
The parison is both stretched and blown to improve strength and clarity.
Commonly used for PET bottles, e.g., soft drink bottles.
Importance of Parison Formation
Determines Final Product Quality
Uniform wall thickness, surface finish, and strength of the final product are influenced by the quality of the parison.
Poorly formed parisons may result in defects like weak spots, uneven thickness, or poor aesthetics.
Material Efficiency
Optimal parison design minimizes material waste and improves cost-efficiency.
Helps manufacturers reduce plastic usage without compromising product performance.
Dimensional Control
Proper parison control ensures the blown product fits the required shape and size accurately.
Critical in applications needing tight tolerances, like automotive components or medical containers.
Process Optimization
Understanding and controlling parison formation aids in faster cycle times and consistent production.
Leads to better productivity and reduced downtime in manufacturing lines.
Customization and Design Flexibility
By controlling parison dimensions (length, thickness, temperature), manufacturers can produce a wide range of hollow objects with complex geometries.
Factors Affecting Parison Formation
Die Design: Influences the flow and shape of the parison.
Melt Temperature and Viscosity: Impacts how uniformly the parison is formed.
Parison Programming: In extrusion blow molding, the wall thickness can be varied along the length of the parison for optimal product performance.
Gravity and Sag: Especially in long parisons, sagging can deform the shape before the mold closes, affecting quality.
Conclusion
Parison formation is a critical step in the blow molding process that significantly affects the quality, efficiency, and economics of manufacturing hollow plastic parts. Mastery of this step allows for enhanced product performance, reduced material usage, and greater control over the final shape and structural integrity of the molded item.