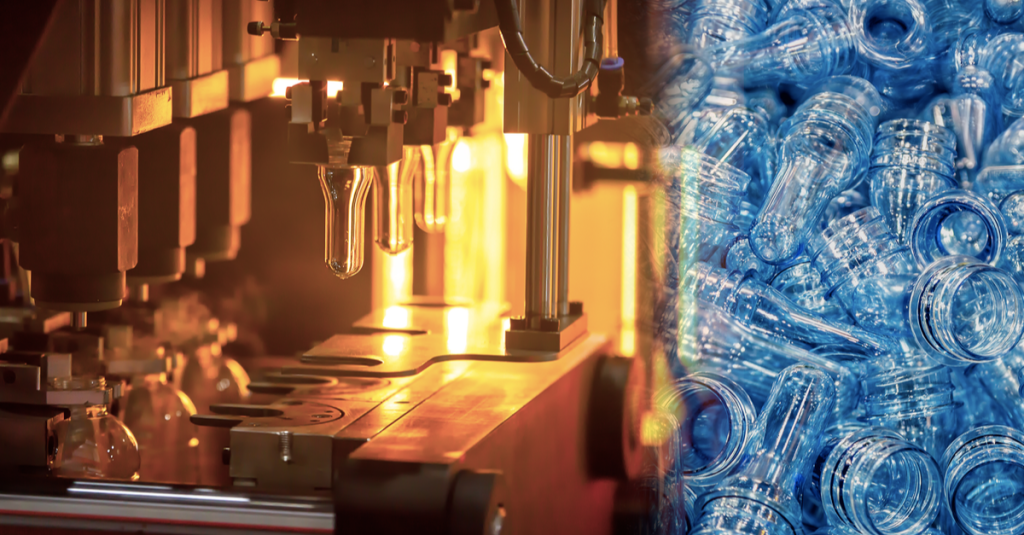
The evolution of injection molding technology reflects a remarkable journey of innovation, driven by material science advancements, industrial needs, and technological breakthroughs. Since its creation in the late 19th century, the process has grown from a simple mechanical operation to a sophisticated and indispensable manufacturing method.
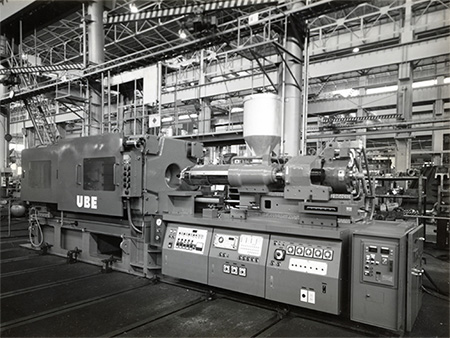
In the 1950s, the introduction of the reciprocating screw machine revolutionized injection molding. This advancement allowed for better melting, mixing, and consistency in plastic materials, paving the way for high-quality mass production. This era also saw the rise of automation, which streamlined operations, reduced labor costs, and increased production capacity. The availability of new polymers like polyethylene and polypropylene during this period further enhanced the versatility of the injection molding process.
By the late 20th century, computer technology had a profound impact on injection molding. Computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) enabled precise mold designs and simulations. These tools allowed manufacturers to identify potential flaws and optimize the molding process before production. The introduction of robotic systems for part removal and assembly also enhanced efficiency, reducing cycle times and improving product quality.
In the 21st century, injection molding has embraced sustainability and smart manufacturing. Bio-based and recycled plastics are increasingly used to meet environmental standards, while advanced molding techniques like gas-assisted and micro-injection molding minimize material use and waste. The rise of Industry 4.0 has integrated smart technologies such as real-time data monitoring, predictive maintenance, and machine learning, optimizing the entire production workflow.
Today, injection molding stands as one of the most efficient and versatile manufacturing processes, capable of producing complex, high-performance components for industries such as automotive, medical, electronics, and consumer goods. Its evolution highlights the interplay between material innovation, engineering ingenuity, and the drive to meet ever-changing industrial demands