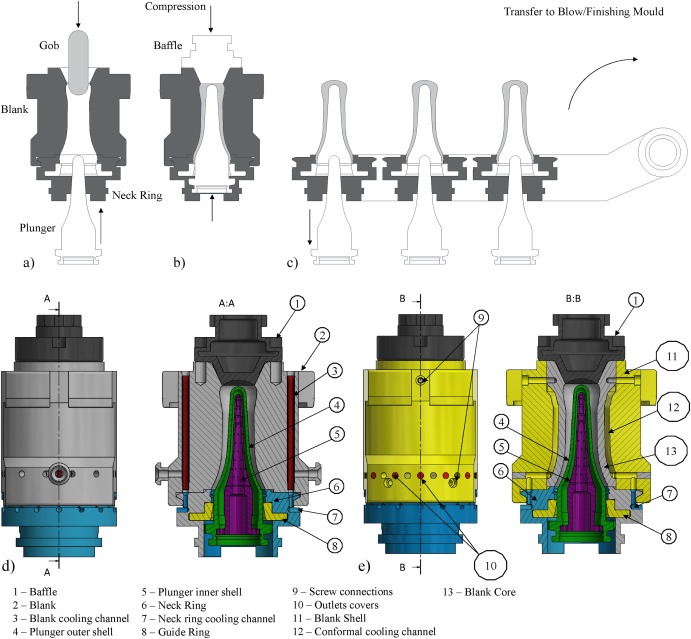
In injection moulding and other mould-based manufacturing processes, efficient cooling system design is crucial for improving product quality, reducing cycle time, and enhancing overall productivity. Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) analysis has emerged as a powerful tool in optimizing mould cooling systems. By simulating heat transfer and fluid flow, CFD allows engineers to predict and improve cooling performance without the need for multiple physical prototypes.
Why Mould Cooling is Important
Cooling is one of the most time-consuming stages in the moulding cycle—often accounting for 60% or more of the total cycle time. Poor cooling system design can result in:
Warpage and residual stresses in the final product
Longer cooling times and cycle delays
Uneven temperature distribution causing inconsistent product quality
Increased energy consumption
An optimized cooling system reduces cycle time, improves part quality, and minimizes waste.
Role of CFD in Mould Cooling Design
1. Simulation of Heat Transfer and Fluid Flow
CFD solves the fundamental equations of fluid dynamics and heat transfer (Navier-Stokes equations) to model:
The flow of coolant through channels
Heat transfer from the mould to the coolant
Temperature distribution across the mould and the product
This allows precise prediction of hotspots, temperature gradients, and inefficient flow zones.
2. Virtual Prototyping
Before committing to expensive physical mould fabrication, designers can use CFD to test multiple cooling channel designs virtually. This reduces trial-and-error and shortens development time.
3. Optimization of Cooling Channel Geometry
CFD helps engineers evaluate:
Conventional straight-line cooling channels
Conformal cooling channels (3D printed to follow part geometry)
Spiral, baffle, and bubbler cooling layouts
By analyzing different designs, engineers can choose the most effective cooling system for uniform temperature control.
4. Evaluation of Coolant Properties
CFD can simulate the performance of different coolants (e.g., water, oil, glycol mixtures) under various flow rates, pressures, and inlet temperatures to optimize thermal performance.
5. Integration with Mould Filling and Warpage Analysis
Advanced simulation tools combine CFD-based cooling analysis with:
Mould filling simulations
Warpage and shrinkage predictions
This comprehensive approach ensures that the cooling system design supports dimensional accuracy and structural integrity.
Benefits of Using CFD in Mould Cooling Design
Improved Part Quality: Uniform cooling minimizes warpage and defects.
Reduced Cycle Time: Optimized heat removal shortens cooling duration.
Cost Savings: Fewer iterations and tooling modifications are needed.
Sustainability: More efficient cooling systems reduce energy usage.
Design Innovation: Enables use of complex conformal cooling channels via additive manufacturing.
Case Example (Optional Section)
Example: A manufacturer reduced cycle time by 20% and warpage by 35% by replacing traditional cooling with a conformal design optimized using CFD. The simulation revealed uneven cooling in the original design, which was corrected through iterative CFD runs.
Conclusion
The use of CFD analysis in mould cooling system design is a game-changer for the manufacturing industry. It enables engineers to design more efficient, reliable, and innovative cooling solutions that improve product quality and reduce costs. As mould geometry and product complexity increase, CFD will continue to be an indispensable tool in mould design optimization.